Google’s search engine is constantly evolving, and as such, so must our SEO implementation. Today I’m going to give you some tips to improve your keyword strategy, content, and link building strategies. We’re not going to reinvent the wheel here, just make some prudent adjustments to improve performance and to address the current state of the Google algorithm. Note this is not a detailed ‘how-to,’ I’m assuming you already know a fair amount about SEO.
Note: This article was updated on September 7th, 2021.
DISCLOSURE: Some of the products mentioned in this post may contain affiliate links that at no additional cost to you, we may earn a small commission. Importantly, we only promote products that we use ourselves.
Keyword Strategy
A lot has been written lately, about how keywords are no longer relevant. This has caused a lot of confusion. I’m here to tell you that keyword strategy still matters! What’s less important, is optimizing content and anchor texts for specific keywords. I’ll touch on that further along in this article.
No matter how you developed your keyword strategy it is always worth a fresh look. Here are some ideas to help you evolve from what you’re doing today:
Poorly Ranking Keywords
Have you been working on a particular keyword for over a year and have been stuck on page 5 the entire time? Like your friends tell you about that ex you’ve had trouble forgetting, it’s time to move on. Remove that keyword from your keyword strategy and don’t put any more effort into it. By all means, leave it in your ranking reports. Let’s invest elsewhere.
Duplicate Keywords
If you have plural and singular or slightly different variations of keywords in your SEO strategy you should remove them (the duplicates). It is true that you may rank differently for each variation but strategically you should not treat these keywords as different providing the variations have exactly the same meaning.
Google Ads/Microsoft Ads Keyword Opportunities
If you’re running paid search campaigns download your keyword performance reports into a spreadsheet. Sort and identify the top-performing keywords by conversions. Remove any that are already part of your SEO strategy and run the rest through any keyword analysis tool (SEMRush, Moz, etc.). Most importantly you want to know where you currently rank and the keyword difficulty relative to other keywords you’ve been able to rank on page 1 for. Identify keywords you believe you can rank on page 1 for and add them to your SEO keyword strategy.
Website Strategy
Google’s new AI and other enhancements are making it less important to include keywords in your content. That is to say, Google understands the meaning of your articles and can rank keywords that don’t even appear in your content. Simultaneously, we are seeing more importance placed on speed, security, and all device usability, i.e. user experience.
In Content
Despite the move away from keyword centric ranking, it is still a good idea to include a few (2 to 3) instances of your primary keyword. Beyond that, you should just write to your readers. Do not place special emphasis on including keywords where they don’t fit, such that it’ll make your writing awkward.
Google has confirmed that they no longer use Hx (heading) or bold/emphasized text in their rankings algorithm. That means you shouldn’t use them either. Heading and bold tags should only be used for formatting your content. If you have old articles where you have bolded all your keywords now is the time to remove those tags. While they probably aren’t harming your SEO, they make your content appear to be written for Google rather than people; that’s not a good thing.
Tags
Page URLs, title tags, and meta descriptions are still primary ranking factors. Do continue to include your keywords in URLs and titles. Description tags should be unique and include a call-to-action to drive higher CTRs (click-through rates). If you get a 10% higher average CTR, for example, you’ll get 10% more organic traffic to your website! The usual rules for the title (50-60 characters max) and description tags (160 characters max), still apply. By the way, you do not need to include your brand or website URL in all your titles. You will probably rank just fine for your brand without that circa 2010 trick. If you’re having trouble fitting your keywords into your title tags, consider removing the brand to free up space. Oh, and always place the brand or ‘standard’ text at the end of your title tag.
Schema, Rich Snippets, Microdata, Open Graph, Etc.
First, none of the structured data elements are used as ranking factors. The painstaking work of adding all the snippets will not, therefore, directly help your search engine rankings. That said, improving the appearance and adding content to what’s displayed in your search engine results will increase your CTR, which means more traffic (Bingo!) and will also have an effect on rankings over time. Major search engines use a common structured data standard. You can use the free structured data markup helper tool from Google to assist in figuring out what tags to include for various pages of your website.
If you use WordPress, I highly recommend using the Rankmath SEO plugin as it includes automatic schema configuration in their free edition.
Obviously, the precision of this tool is not going to be as good as doing it manually. But if you have hundreds of articles who wants to spend days tagging everything?
If you want to also include tags for Facebook’s Open Graph and Twitter’s card metadata you can simply turn those features on in Rankmath or SEO Yoast if you prefer that tool.
Website Performance
Over the past few years, Google has placed more emphasis on website speed, compatibility, and security. Some factors matter more than others.
Load Time & UX
User Experience and raw load times have become more important over the years.
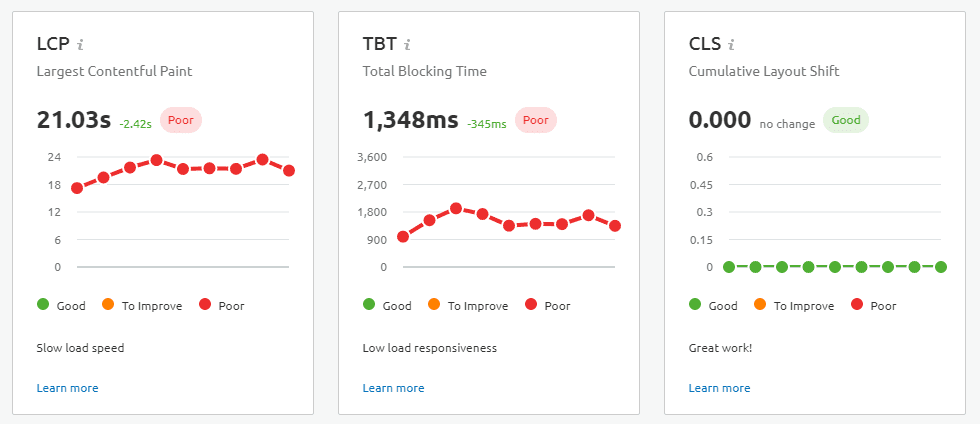
This is most evident with the launch of Google’s new Core Web Vitals tool. Core Web Vitals reports offer metrics for Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) and First Input Delay (FID). In combination, these describe how users experience the loading speed/time for your website. In addition, Core Web Vitals includes a report on Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). This indicates if page elements suddenly shift after the page has completed loading.
It’s crucial to use this tool to assess your site. If you score poorly you need to make some technical improvements to your site to raise your scores. The tool is available in Search Console and through some 3rd parties; SEMrush includes it in their site auditing toolset.
Security
In 2015 Google announced that secure websites (using https://) would rank better, and they are. Also, since Chrome browser users will now see security warnings for non-https sites, it’s going to cost you visitors if you don’t certify your site. Certificates are mostly included for free by web hosts these days.
Device Compatibility
Mobile! If your website is not mobile compatible this should be your top priority for SEO. Even if you aren’t taking a big mobile rankings ‘hit’ you may be scaring arriving mobile visitors away. If people have to start zooming in on their iPhone to fill in your form you are losing conversions – period! The best mobile solution is to make your website adaptive. If you use a CMS like WordPress it is a matter of installing and configuring any adaptive theme. As with security, this may not be so straightforward; better get a few quotes before you begin.
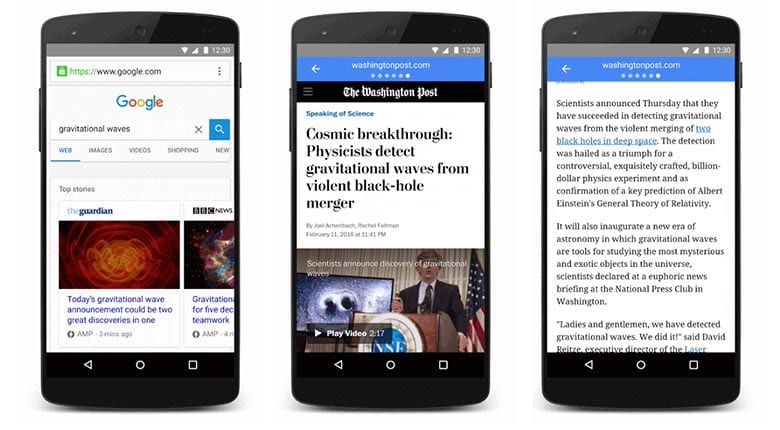
The other part of mobile compatibility worth considering is making your website AMP compatible. AMP is still not a factor in rankings, but the enhanced presentation of your search results and better user experience can lead to higher CTRs and longer/better engagement with your content. Those are factors for better rankings. Setting up AMP in WordPress is as easy as installing a plug-in. AMP may require heavy lifting for other CMS platforms and simple HTML websites. Best check with, you guessed it, your web dev for some guidance.
Markup
If your website looks good on all devices, loads fast, and is secure you are done for now. HTML markup errors don’t make a lick of difference to SEO. Obviously, broken functionality needs to be fixed, but just having ‘clean’ code is not at all important.
Offsite SEO
Google is doing more of the same when it comes to backlink analysis. This simply means that they have become more aggressive at penalizing link exchanges, over-optimized anchor texts, links that are plainly low-quality, and the like.
Link Disavow and Removal
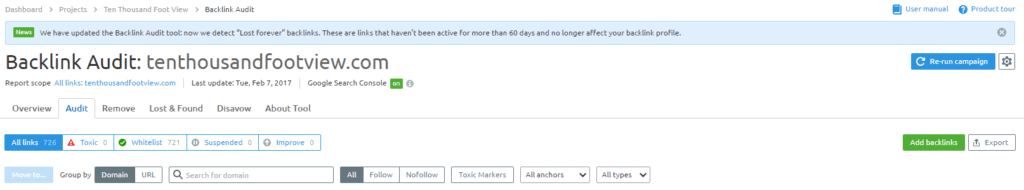
Several years ago, ‘link disavow and removal’ came on the scene as a one-time service to get rid of all those junk links you’d built in the past. Fast forward a few years and link disavow is a recurring task that should be implemented on an as-needed basis. There are a number of ways you can quickly and easily implement link disavow, while removal is a bit more of a daunting (unnecessary) task. You can find a service provider to perform this for you as needed, or employ an automated tool and do it yourself. I seem to be giving a lot of shout-outs to SEMrush, but they do have an amazing tool for managing the entire disavow process.
Link Building
As I like to tell my clients, I build links like its 2025. While it’s impossible to future proof link building, it’s a foregone conclusion that Google will do a better job of finding artificial links in the future. What is an artificial link? It’s any link you get that you paid for (whether that link is directly paid for or you pay for somebody to create properties and respective backlinks on those properties). Yes, 100% of link building, outside of outreach, is not allowed according to Google.
That point aside, link and anchor text diversification is the most important element of ‘clean’ link building. Build many different types of links over a long period of time. A good backlink profile will contain about 40% of branded, 40% of keyword, and 20% randomized anchor texts. Does it matter if it’s split 20/35/45? Not so much, but ensure you have a healthy volume of each type. Furthermore, links should be built on different networks but mostly in your country of interest. If you are targeting the US and 95% of your links are based in China you have a big problem. Here’s a good breakdown of different link building strategies and structures for variety:
- Local SEO (citation links are crucial if you serve a small geographic market)
- Contextual links, aka link wheels (very diverse link building that looks natural, your core link building strategy)
- High domain authority links (a lot of link juice from individual links, but use sparingly)
- Guest posts (high relevance backlinks, work very well if you are having trouble ranking a specific keyword)
- Press Releases (use a reputable distributor and don’t overdo it with too many of these)
Summary
In a way, SEO has become more simplistic. Write for users instead of search engines, make your website run fast and look great on all devices. Build a wide range of backlinks with diverse anchor texts. Target the right keywords in your content, but don’t load up on them… keep it natural (looking) and your rankings will soar.
Need help with your company’s SEO? Check out our Search Engine Optimization services.